Attention
This website is best viewed in portrait mode.
Publication Name: Financialexpress.com
Date: January 26, 2025
Battery passport: Revolutionizing lifecycle management, transparency, and compliance across supply chains
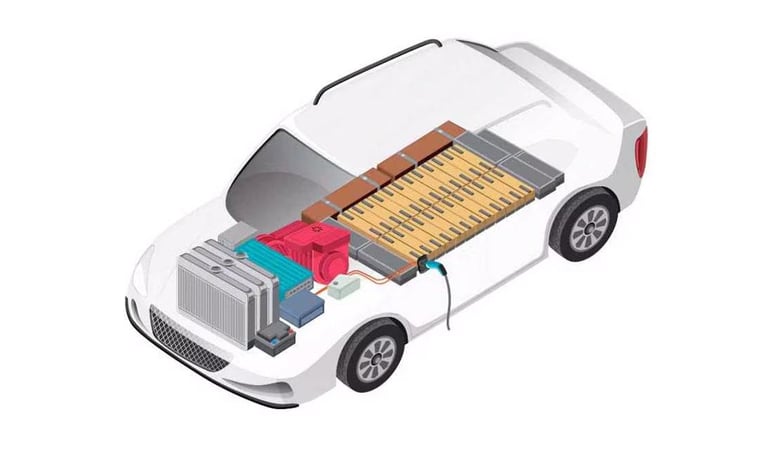
A battery’s lifecycle starts from sourcing raw materials to its eventual disposal or recycling.
The accelerating global transition to electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy has brought batteries to the forefront as a critical component of sustainable infrastructure. However, the complexities surrounding their production, usage, and disposal demand innovative digital solutions. Enter the “Advanced Battery Passport,” a transformative digital tool designed to ensure lifecycle management, transparency, and regulatory compliance across supply chains. It also pushes the boundary for the OEM and battery manufacturers by unlocking insights from data to take decisions.
Driving Enhanced Lifecycle Management Through Transparency and Traceability
A battery’s lifecycle starts from sourcing raw materials to its eventual disposal or recycling. Transparency across this chain is pivotal to address ethical, environmental, and operational concerns. Battery Passport provide a digital identity for each battery, encapsulating data about its origin, material composition, manufacturing process, usage patterns, and end-of-life handling. This detailed traceability enables stakeholders to identify sources of inefficiency, assess sustainability metrics, and ensure adherence to international standards.
For instance, a digital battery passport can track the critical minerals such as cobalt or lithium used on the batteries from mining to deployment, highlighting whether the raw materials were ethically sourced and processed without environmental violations. This transparency empowers manufacturers, regulators, and consumers with actionable insights, laying the groundwork for a more sustainable industry.
Blockchain Integration: Ensuring Data Security and Immutability
At the core of the battery passport’s functionality lies data integrity. Blockchain technology, with its decentralized and immutable structure, ensures that the recorded data remains secure and untampered. Unlike centralized databases prone to breaches and ownership disputes, blockchain allows multiple stakeholders—from raw material suppliers to vehicle manufacturers—to contribute to and access the shared ledger without compromising data confidentiality.
Furthermore, blockchain-based smart contracts can automate compliance checks and streamline reporting, reducing administrative overheads. Coupled with emerging standards like the Catena-X protocol, Digital Battery passport promises seamless data exchange within the automotive ecosystem, bolstering both security and collaboration.
Promoting Sustainability and Optimizing Manufacturing Processes
Sustainability is at the heart of the battery passport initiative. By providing comprehensive data on material efficiency and carbon emissions, these passports enable stakeholders to measure and mitigate environmental impact. For example, insights from battery passports can encourage the use of recycled materials, reducing reliance on virgin resources. They can also help manufacturers optimize energy use during production and identify inefficiencies in battery performance.
Additionally, the passport facilitates end-of-life decision-making, such as determining whether a battery should be recycled, repurposed for energy storage, or disposed of safely. This promotes circularity by ensuring that valuable materials are reintegrated into the supply chain, minimizing waste and conserving resources.
Demonstrating Compliance with Evolving Regulations
As nations adopt stringent environmental policies, the battery passport serves as a critical tool for regulatory compliance. The European Union’s forthcoming Digital Product Passport (DPP) regulations, for instance, mandate transparency in material sourcing and carbon footprint reporting. Similarly, India’s Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) framework shifts accountability for battery disposal from manufacturers to vehicle producers, underscoring the need for robust traceability mechanisms. By standardizing data reporting and ensuring traceability, manufacturers can seamlessly meet compliance requirements, reducing risks of non-conformity and enhancing global trade capabilities.
Battery passport simplifies adherence to these complex frameworks by consolidating all compliance-related data into a single digital profile. This ensures that manufacturers and suppliers can meet evolving global standards without incurring significant administrative costs.
Data to Decisions: Value beyond compliance
Beyond meeting regulatory requirements, the Battery Passport unlocks significant value through advanced analytics. By transforming raw data into actionable insights, it empowers manufacturers to predict performance trends, optimize production, and reduce costs. Fleet operators can use analytics to monitor battery health and schedule proactive maintenance, while energy providers can assess second-life applications for used batteries.
These analytics-driven solutions not only improve operational efficiency but also enhance customer experiences, creating a more sustainable and profitable battery ecosystem.
Future Prospects: Transforming the Supply Chain
The industrial potential of battery passports extends beyond compliance. By fostering data transparency and collaboration, they pave the way for innovations in supply chain management. For example, real-time data analytics powered by battery passports can optimize logistics, improve material recovery rates, and enable predictive maintenance strategies.
Moreover, the insights derived from these digital tools can guide research and development, helping manufacturers adopt next-generation materials and technologies. The resulting efficiencies—both operational and environmental—promise to lower costs and enhance sustainability across industries.
Path Forward
Digital battery passport is more than a regulatory requirement; it is a cornerstone of the sustainable energy transition. By integrating advanced technologies like blockchain and embracing circular economy principles, it addresses the pressing challenges of resource scarcity, environmental degradation, and ethical sourcing. As global supply chains become more interconnected, the adoption of battery passports will not only ensure compliance but also unlock unprecedented opportunities for innovation and growth. With the right policy support and industry collaboration, this digital revolution can drive a more sustainable and equitable future.
Author: Anil Radhakrishnan, Chief Product Officer, Tata Elxsi