Attention
This website is best viewed in portrait mode.
How Industry 4.0 is Transforming the Manufacturing Industry
In an interaction with CIOReview India, Aditya Chikodi, General Manager and Business Head for Innovation and Design at Tata Elxsi, shares his thoughts on how Industry 4.0 is transforming the Manufacturing Industry and helping achieve sustainability in business practices.
Industry 4.0 market size is projected to reach USD 222.4 Billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 19.6% from 2021 to 2028. How do you see this market evolving in India?
From the perspective of India, we must take a step back and observe how the entire Indian environment is organized. In 2017-2018, the Indian government unveiled an ambitious aim to increase the manufacturing sector's contribution to GDP from around 17% at the time to over 25% by 2022. Industry 4.0 can provide the country’s manufacturing sector the much-needed platform to stay competitive in the global market. The key areas that need to be addressed by industry 4.0 implementation are health and safety of workers, cost reduction and production optimization, and value addition like custom manufacturing.
However, with MSME accounting for nearly half of Indian manufacturing output and 40% of exports, we must make industry 4.0 technologies available to 50 million or more businesses. Bringing the Indian MSME sector to the forefront of the fourth Industrial Revolution will necessitate a significant investment in terms of funds, infrastructure, technical know-how, and exposure.
In this regard, the Indian government will play a crucial role. Similar initiatives have occurred in other countries, such as the United States, which refers to it as Smart Manufacturing, China, which refers to it as Made in China 2025, and here in India, we refer to it as Make in India or Digital India.
The government of India has launched the SAMARTH (Smart Advance Manufacturing & Rapid Transformation) initiative, which aims to bring together the ecosystem of manufacturers, vendors, customers – key stakeholders – and create demonstration and experiential centres to spread awareness of I4.0. Center for Industry 4.0 (C4i4) Lab Pune, IITD-AIA Foundation for Smart Manufacturing are two examples.
Furthermore, India's IT industry is now at a critical crossroads to contribute to and assist the transformation required for India to become a big player in the manufacturing sector. With the assistance of both the government and the business sector, India has the potential to become one of the world's manufacturing leaders in the coming decade.
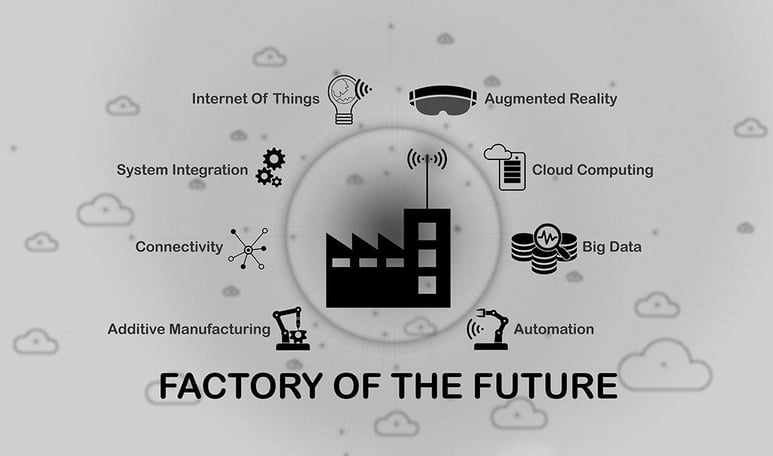
The term Industry 4.0 includes a variety of key enabling technologies such as cyber-physical systems, IoT, AI, big data analytics, and digital twins which can be considered as the major contributors to automated and digital manufacturing environments. Please elaborate on how Industry 4.0 technologies would help achieve sustainability in business practices.
The financial, legal, and regulatory environment in which manufacturers operate today is changing all over the world. Unlike a few years ago, businesses are now viewing sustainability as a key metric and are monitoring it. We see that over $1 trillion in ESG investments are estimated to be channeled to organizations that have committed to the UN Sustainable Development Goals.
Let’s look at some statistics. We are seeing supply chain issues that have hampered over 95 percent of Fortune 1000 organizations. Industries account for around 35-40% of CO2 emissions. By 2030, there will be a 2.4 million labour shortfall in India alone. Furthermore, increasing consumer awareness and perception of the impact on our environment in general has become critical, making it increasingly important for businesses to consider sustainability as a practice.
A shift toward smart connected sustainable manufacturing could help address these issues, and Industry 4.0 is an important step in that direction. In a nutshell, Industry 4.0 is the integration of manufacturing and information technology to create a flexible, adaptable, connected, and responsive cyber-physical environment that delivers consistent economic value and a great customer experience. When you consider the whole sustainability factor, there are at least 10 different SDG goals that would be positively impacted by the application of Industry 4.0.
In a connected supply chain, for example, the entire production plant can be repurposed based on actual demand rather than having a single configuration targeting one product of a given lot. This will result in a system that is modular and interoperable enough to allow the line to be repurposed based on actual market need, leading to optimized usage of resources.
Such examples prove that the application of industry 4.0 technology - either a part of it or the whole of it is going to create a positive impact but with the required investments.
Where do you see the market for Industry 4.0 in the near future?
Industry 4.0 will deliver value around six key principles: Interoperability, Virtualization, Decentralization, Modularity, Real-time capability, and Service Orientation. These six principles, supported are paving the path towards a digital future.
The adoption of the industrial internet is increasing, and this is one of the major factors driving the growth of the global Industry 4.0 market. Furthermore, the increasing adoption of automation for high-quality production is expected to ensure market growth in the coming years.
At the moment, more than 5.8 billion endpoints are linked through IIoT systems. We shall see the deployment of technologies in digitization and the establishment of a linked shop floor in the next 1-3 years. IT-enabled supply chain integration has been ongoing for some time. The main difference now is that it is faster, and manufacturers are considering integrating the entire supply chain.
On the IT side, we will witness IT/OT convergence, and these will begin to merge sometime in the future years. Organizations are investing money into training to close skill gaps. One of them is the automobile business, which is aggressively using cobots and other automation characteristics.
Going forward, the near future will be about better educating the workforce on manufacturing priorities and processes in order to empower them in the digital transformation path to the point of connecting and automating the shop floor. Extracting data and creating insights at the plant level in order to incorporate it into the end-to-end supply chain must be done simultaneously.